Dna Codes for Proteins Which Are Used to
A protein that can be used to treat a disease. In prokaryotes genes tend to be represented by contiguous bases in the DNA with promoter and other transcription factors nearby.
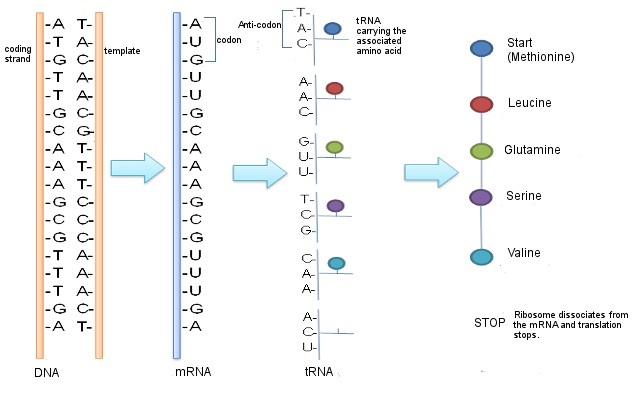
How Do Genes Direct The Production Of Proteins Mt Hood Community College Biology 102
3A GCTIACGGGA GTCTCTACATIGGGTA ACT 5 mRNA.

. The idea Birney said in 2012 is that the 8 is nearly all regulatory sequences DNA that governs the behavior of the 1 percent of DNA that codes for proteins. Genetic code is the term we use for the way that the four bases of DNAthe A C G and Tsare strung together in a way that the cellular machinery the ribosome can read them and turn them into a protein. So each sequence of three codes for an amino acid.
Genetic code is the term we use for the way that the four bases of DNA--the A C G and Ts--are strung together in a way that the cellular machinery the ribosome can read them and turn them into a protein. In the genetic code each three nucleotides in a row count as a triplet and code for a single amino acid. TAC AGT TCC GAC ATC ATG AGG ATT 3.
DNA is the code to life and the body creates different proteins from its instructions. TAC AGT CCG TAG TGA ATT 2. Sentences with DNA codes 1.
The bases are Adenine A Thyamine T Cytosine C and Guanine G. DNA to RNA to Proteins Concept. Every chain has four seperate components.
DNA is a sequence of 4 different bases A T G and C. A protein that has an interesting shape. The DNA remains in the cell nucleus but the production of the protein occurs in the cytoplasm.
Ethanol decreases CO2 production. It is widespread but not universal. The accurate synthesis of proteins thus is.
This requires the help of mRNA. Introduction DNA is the code of life. Each amino acid is represented by a code of three nucleotides known as a codon.
If you took two bases to code for each amino acid that would still only give you 16 possible codes TT TC TA TG CT CC CA and so on - still not enough. Examples of specialized RNA molecules produced from noncoding DNA include transfer RNAs tRNAs and ribosomal RNAs rRNAs which help assemble protein building blocks amino acids into a chain that forms a protein. TAC AAA CCC AGC ATT 4.
DNA has the code for a protein which mRNA has to copy and then take that copy out of the nucleus to an other organelle called a ribosome. DNA has the code for a protein which mRNA has to copy and then take that copy out of the nucleus to an other organelle called a ribosome. Ala Arg Asn Asp Cys Gln Glu Gly His Ile Leu Lys Met Phe Pro Ser Thr Trp Tyr Val.
Messenger RNA substitutes a U for the T when the copy is made but you still have only 4 possible choices in your code. The following piece of DNA codes for a protein. However the bases of RNA differ from those of DNA in that thymine T is replaced by uracil U in RNA.
And long noncoding RNAs lncRNAs which are longer. Thats enough to code for everything with lots to spare. DNA codes for proteins in a cell by arranging certain nitrogen bases of the cell in a particular order.
For many years scientists looked for the answer of what holds the information for life to occur. How many amino acids are in this protein. In the genetic code each three nucleotides in a row count as a triplet and code for a single amino acid.
DNA is the chemical used to store genetic information inherited traits and characteristics in the body. The sections of DNA that code mRNA are known as protein coding regions. A U G and C.
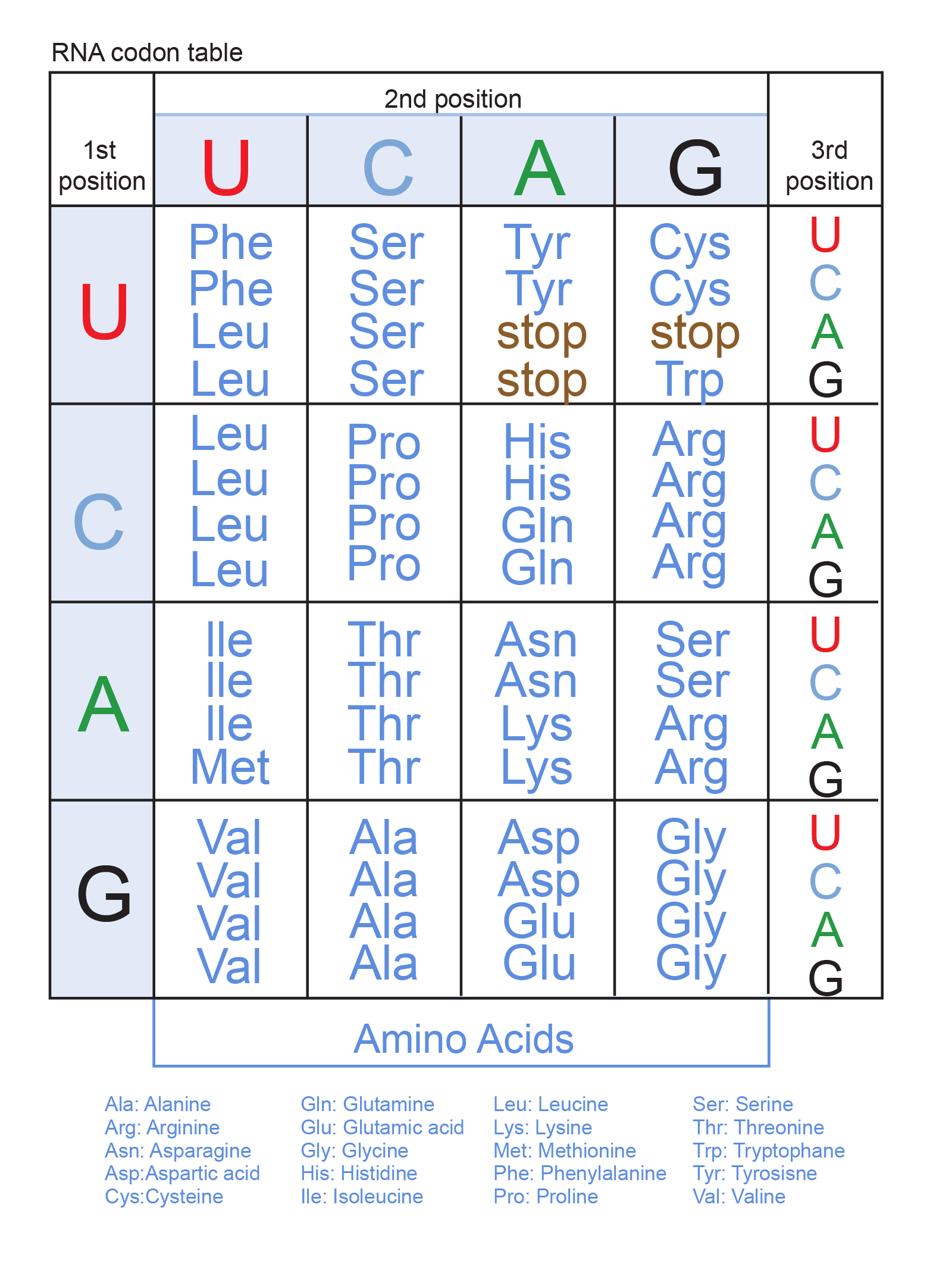
Similarly how are proteins synthesized in a cell. The genetic code that represents the 20 amino acids is shown in figure 1. The shape of DNA is a double helix two complementary chains interwoven.
Ethanol is clean energy from corn. RNA is a molecule that is chemically similar to DNA and also contains repeating nucleotide subunits. What does a pair with in DNA.
The process of converting DNA into RNA is called transcription. Enzymes give 4 characteristics of the genetic code it is a triplet code. Each of those triplets codes for a specific amino acid.
TAC TTA TCC TCG TGG TTT TAA ATT 5. Some codes dont correspond to an amino acid but indicate stop. Transcription begins near a promoter site and ends at a terminator site.
The amino acids are the building blocks of the proteins. Specifically messenger RNA mRNA carries the protein blueprint from a cells DNA to its ribosomes which are the machines that drive protein synthesis. However if you took three bases per amino acid that gives you 64 codes TTT TTC TTA TTG TCT TCC and so on.
Although DNA stores the information for protein synthesis and RNA carries out the instructions encoded in DNA most biological activities are carried out by proteins. Why is RNA used in protein synthesis instead of DNA. Which of the following is a circular DNA from bacteria that can hold a foreign gene.
Protein synthesis is the. Proteins are made from 20 main amino acid molecules. Each triplet of bases codes for one particular amino acid.
How DNA Encodes for Proteins. A section of DNA a gene that codes for a protein. During transcription DNA is converted to messenger RNA mRNA by an enzyme called RNA polymerase.
After many experiments scientists realized that DNA holds this necessary. The code is then read by transfer RNA tRNA molecules in a cell structure called the ribosome. Use the codon chart to determine the amino acid sequence of this protein.
RNA lets DNA stay in the cell while RNA duplicates and transfers copied versions of DNA. The process of coding protein with the reading of mRNA is called translation. The mRNA specifies in triplet code the amino acid sequence of proteins.
DNA RNAProtein These are the steps. DNA is the molecule of life. MicroRNAs miRNAs which are short lengths of RNA that block the process of protein production.
There the copy is translated into the protein. Structural proteins including collagen and keratin. These amino acids are added one by one to form a protein.
It is a degenerate code. TAC CGG CCC CGT ATT 6. This is how it works.
To enable genes to code for proteins the bases A T G and C get together - not in pairs - but in triplets. It defines how the four-letter code of DNA is translated into the twenty-letter code of amino acids. In DNA the code letters are A T G and C which stand for the chemicals adenine thymine guanine and cytosine respectively.
Comments
Post a Comment